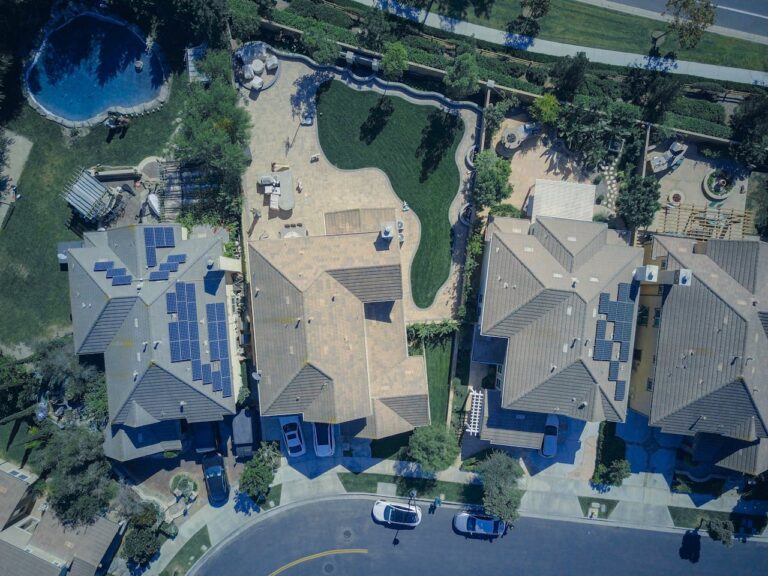
When you sell a home, understanding capital gains tax is crucial. This tax can impact how much profit you keep. Let’s break it down in simple terms.
What is Capital Gains Tax?
Capital gains tax is a levy on the profit from selling an asset. It’s the difference between the purchase price and the selling price. If you sell your home for more than you paid, the profit might be subject to tax.
How Does Capital Gains Tax Work?
When you sell your home, any profit you make is called a capital gain. This gain is taxed differently based on how long you owned the home.
- Short-Term Capital Gains: If you owned your home for one year or less, the gain is taxed as ordinary income. That means it could be taxed at a higher rate.
- Long-Term Capital Gains: If you owned your home for more than a year, you benefit from lower tax rates. These are typically 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on your income.
Are There Exceptions to Capital Gains Tax?
Yes, there are exceptions, especially for homeowners.
- Primary Residence Exclusion: If you’ve lived in the home for at least two of the last five years, you might exclude up to $250,000 of the gain ($500,000 for married couples) from your taxable income.
- Investment Properties: Different rules apply, and you might not qualify for the primary residence exclusion.
How to Calculate Capital Gains Tax
Calculating your capital gains tax involves a few steps:
- Determine Your Cost Basis: Start with the purchase price of your home. Add any improvements or fees, like closing costs. This total is your cost basis.
- Calculate the Gain: Subtract the cost basis from the selling price of your home. This is your capital gain.
- Apply Exclusions: If eligible, subtract the primary residence exclusion from your gain.
- Determine the Tax Rate: Based on your income and how long you owned the home, apply the appropriate tax rate to the remaining gain.
How Can You Avoid Capital Gains Tax?
There are strategies to minimize or avoid capital gains tax legally:
- Live in the Home Longer: Meet the two out of five years residency requirement to qualify for the exclusion.
- Offset Gains with Losses: If you have investments that lost money, you can use those losses to offset your gains.
- Consider a 1031 Exchange: If selling an investment property, reinvest the proceeds into a similar property to defer taxes.
What Are the Benefits of a 1031 Exchange?
A 1031 Exchange allows you to defer paying capital gains tax on an investment property. Here’s how it works:
- Reinvestment: You must reinvest the proceeds into another “like-kind” property.
- Timing: The new property must be identified within 45 days and purchased within 180 days of the sale.
This strategy can be complex, so consult with a tax advisor to ensure compliance.
What Mistakes Should You Avoid?
Avoid these common pitfalls:
- Ignoring the Two-Year Rule: Not meeting the residency requirement can lead to higher taxes.
- Miscalculating Improvements: Only major renovations add to your cost basis, not routine maintenance.
- Overlooking State Taxes: Some states have their own capital gains tax, so check local laws.
How Can Technology Help with Capital Gains Tax?
Technology can simplify tracking and calculating capital gains tax:
- Capital Gains Calculators: Online tools can estimate your tax liability.
- Digital Record Keeping: Use apps to track home improvements and expenses, ensuring accurate cost basis calculations.
What Questions Should Home Sellers Ask?
- Do I Qualify for the Primary Residence Exclusion? Understand the eligibility requirements to maximize your savings.
- What is My Cost Basis? Accurately calculating this can reduce your taxable gain.
- How Does My Income Affect My Tax Rate? Knowing your tax bracket helps estimate your liability.
Stay Informed: How Can You Keep Up with Changes?
The real estate tax landscape changes. Staying informed is vital:
- Read Industry Blogs: They provide updates on tax laws and strategies.
- Attend Seminars and Webinars: These events offer insights into real estate and tax planning.
- Consult Tax Professionals: Regularly check with tax advisors to keep your strategies current.
Why Understanding Capital Gains Tax Matters
Knowing about capital gains tax is essential for home sellers. It impacts your profits and planning. By understanding the rules and strategies, you can optimize your tax situation. Always consider consulting with a tax professional to ensure you’re making the best decisions for your unique circumstances.
For more key terms and information, visit our Glossary of Key Terms for Home Sellers.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can effectively navigate the complexities of capital gains tax. Whether you’re selling your primary residence or an investment property, understanding these principles ensures that you make informed decisions and maximize your financial gains.